How to Pass the OLSAT Test Levels E and F in 2025
Updated November 5, 2024
- What Are the OLSAT Level E and OLSAT Level F?
- What Do the OLSAT Otis-Lennon Tests Assess?
- What Type of Questions to Expect on the OLSAT Test Level E and F in 2025
- OLSAT Otis-Lennon School Ability Test Score Interpretation
- Free OLSAT practice test (Level E & Level F)
empty
empty
empty
empty
- How to Prepare for the OLSAT Level E and F in 2025
- How Are the OLSAT Level E and OLSAT Level F Scored?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Final Thoughts
What Are the OLSAT Level E and OLSAT Level F?
The OLSAT (Otis-Lennon School Ability Test) is a multiple-choice test that is used to assess children for gifted and talented programs or to support an application for specialized schools.
The OLSAT is split into different levels: level A through to level G. Each level is aimed at a different age group:
- OLSAT Level E is administered to students in 4th and 5th grade (9–11 years old)
- OLSAT Level F is for students in 6th, 7th and 8th grade (11–14 years old)
The Level E and F tests are together in this article, as they have the same number of questions on the same topics, split into verbal and non-verbal.
From Level E, the assessments are different from the previous levels – they are designed to reflect the learning potential and maturity of the students from the 4th grade, including deep analytical skills and more sophisticated problems.
With previous levels, questions on the OLSAT are more about following directions and questions based on pictures, with verbal instructions used.
What Do the OLSAT Otis-Lennon Tests Assess?
The OLSAT Levels E and Level F are based on questions that assess aptitude rather than intelligence – the test aims to provide an idea of what a student is capable of, rather than what they have learned in school so far.
The assessment evaluates a student based on their reasoning and critical thinking skills by using questions that draw out examples of memory and the ability to see patterns and relationships.
The test is taken in a group setting and can be completed online or using pencil-and-paper.
What Type of Questions to Expect on the OLSAT Test Level E and F in 2025
The latest version of the Otis-Lennon School Ability Test is OLSAT 8, which has several levels, including OLSAT 8 Level E and OLSAT 8 Level F, designed for use with students in grades 4 and 5, respectively.
The updated version aims to enhance the accuracy and reliability of the assessment, providing educators with valuable insights into students' cognitive abilities.
There are 72 multiple-choice questions on the OLSAT Levels E and F, with 36 verbal and 36 non-verbal, and a time limit of 60 minutes.
As this is a test for potential rather than learned knowledge, students will not be able to take any tools into the test area, regardless of whether they are taking the test via paper and pencil or online.
In previous levels, aimed at the younger students, some of the questions might be read out in a one-on-one setting, but from Level E the child is responsible for reading and completing the exam on their own.
OLSAT Otis-Lennon School Ability Test Score Interpretation
There are three stages to the scoring system on the Otis Lennon tests.
The first is the raw score, which is a simple representation of the number of correct answers in each section.
The maximum score is 60, with 30 from the verbal section and 30 from the non-verbal section. The OLSAT is not negatively marked, which means there are no penalties like a point being taken away for a wrong answer.
The second part is the School Ability Index (SAI). This score is calculated by comparing the raw score to other same-aged children’s scores to find where they rank.
The SAI has a maximum score of 150 and an average score of 100, with a standard deviation of 16.
The final score of the OLSAT is the percentile score, which compares the students in the same grade and age group against each other.
This is shown as a percentage, so if a child scores in the 76th percentile, it means that they have performed better than 76% of their cohort.
It is difficult to pinpoint what OLSAT score is “gifted” – the requirements for each gifted and talented program or specialized school will vary.
But it is generally accepted that a score that is two standard deviations from the mean in the SAI (so 132 or above) is the minimum requirement. This equates to a score in the 97th percentile or above.
Prepare for OLSAT Test Level E and F with Test Prep Online
Free OLSAT practice test (Level E & Level F)
Here are some sample questions for practice for the OLSAT test (grade 4 through 8):
OLSAT Verbal Comprehension
Verbal comprehension questions assess the student on their ability to understand words and manipulate them in different contexts.
OLSAT Antonyms
These are vocabulary-based questions, asking the student to identify words that have opposite meanings, which is considered harder than identifying synonyms.
1. Which word is an antonym of ‘soft’?
a) Gentle
b) Hard
c) Kind
d) Tall
OLSAT Sentence Completion
In these questions, the student needs to select the word that completes the sentence in a correct and meaningful way that makes sense.
1. Complete this sentence:
The quick red fox ______ over the lazy brown dog.
a) Slept
b) John
c) Beautiful
d) Jumped
Sentence Arrangement
This is a similar type of question to the sentence completion, but instead of inserting a single missing word to make a sensible sentence, here the sentence needs to be put together in the right order.
1. Rearrange the words to fit the sentence in the right places:
It ______ a beautiful, ______ ______. All was still and ______.
a) Silent
b) Was
c) Morning
d) Warm
OLSAT Verbal Reasoning
Verbal reasoning is about deducing relationships, making comparisons and drawing conclusions with language.
OLSAT Arithmetic Reasoning
Although this type of problem includes numbers, it is not focused on the computational ability of the student – more about their ability to use numbers to draw conclusions.
1. Amy, Laura and Sarah want to share some candy equally, and there are 12 pieces in total. How much do they get each?
a) 3
b) 6
c) 12
d) 4
OLSAT Logical Selection
In the logical selection section, the student needs to complete a statement or a sentence using simple logic.
1. The animal has soft fur, but it has needle-sharp claws. Some types have been domesticated and are common house pets, but many live wild and can be found in zoos.
a) The animal is a cat
b) The animal is a giraffe
c) The animal is a bear
d) The animal is a lizard
OLSAT Word and Letter Matrix
Presented as a 3 x 3 square, the matrix has eight related words or letters that form a pattern both horizontally and vertically.
The student needs to use this pattern to find the missing item in the matrix.
1. Fill in the missing word in the matrix below:
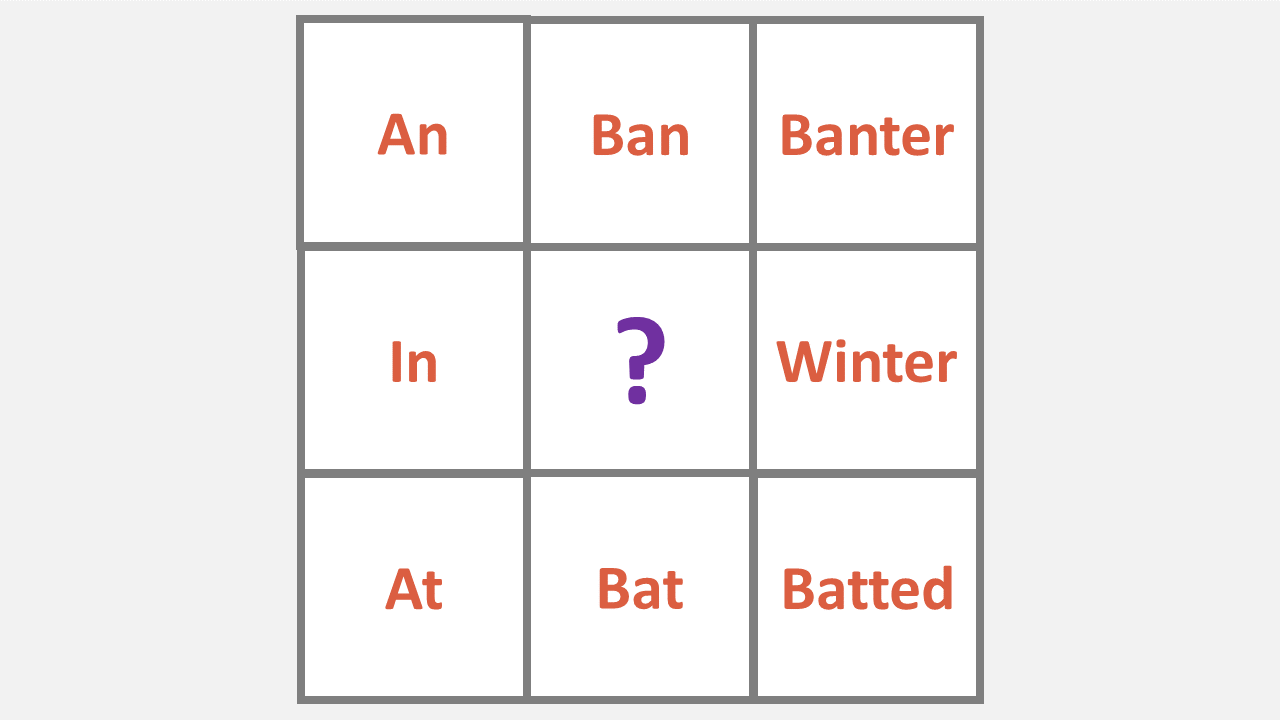
a) Tin
b) Win
c) Wan
d) Kin
OLSAT Verbal Analogies
The student is presented with a pair of words that are related to each other in the same way and must find a second pair in the multiple-choice options that are related in the same way.
1. 'Up' is to 'down' as 'warm' is to:
a) Far
b) Near
c) Cold
d) Hot
If you want 12-month access to all the practice resources for this test, our partner TestPrep-Online.com offers a Family Membership.
Family Membership gives you access to all the TestPrep-Online resources for the next 12 months. You will also get two separate accounts, which can be very helpful if you have two children preparing for their tests.
Get a Family Membership with 12-month access
OLSAT Verbal Classification
Classifying words by what makes them the same is what this question is looking for – by asking the student to spot the odd word out from a group.
These questions test whether the student understands how words are classified; the student must show this by selecting the odd word out.
1. Which is the odd word out of the group below?
a) Wheel
b) Axle
c) Engine
d) Bed
OLSAT Inference
Inference is the skill of reaching a conclusion based on a syllogism – the student is given basic propositions and needs to follow the logic to infer the correct answer.
1. Anne, Laura and Amanda own horses, and Amanda has the most. If Anne has two horses, we know for certain that:
a) Laura also has two horses
b) Amanda has seven horses
c) Amanda has more than two horses
d) Amanda has no horses
OLSAT Figural Reasoning
What is being assessed in the figural reasoning section of the OLSAT is determining relationships between geometric figures by understanding patterns, figure manipulation and working in a spatial context.
OLSAT Figural Analogies
Figural analogies are like verbal analogies but without words – if A is to B as C is to D, what is D?
In these questions, students needs to pick the missing figure.
1. Considering that Figure 1 is to Figure 2 as Figure 3 is to Figure 4, choose what should be Figure 4.
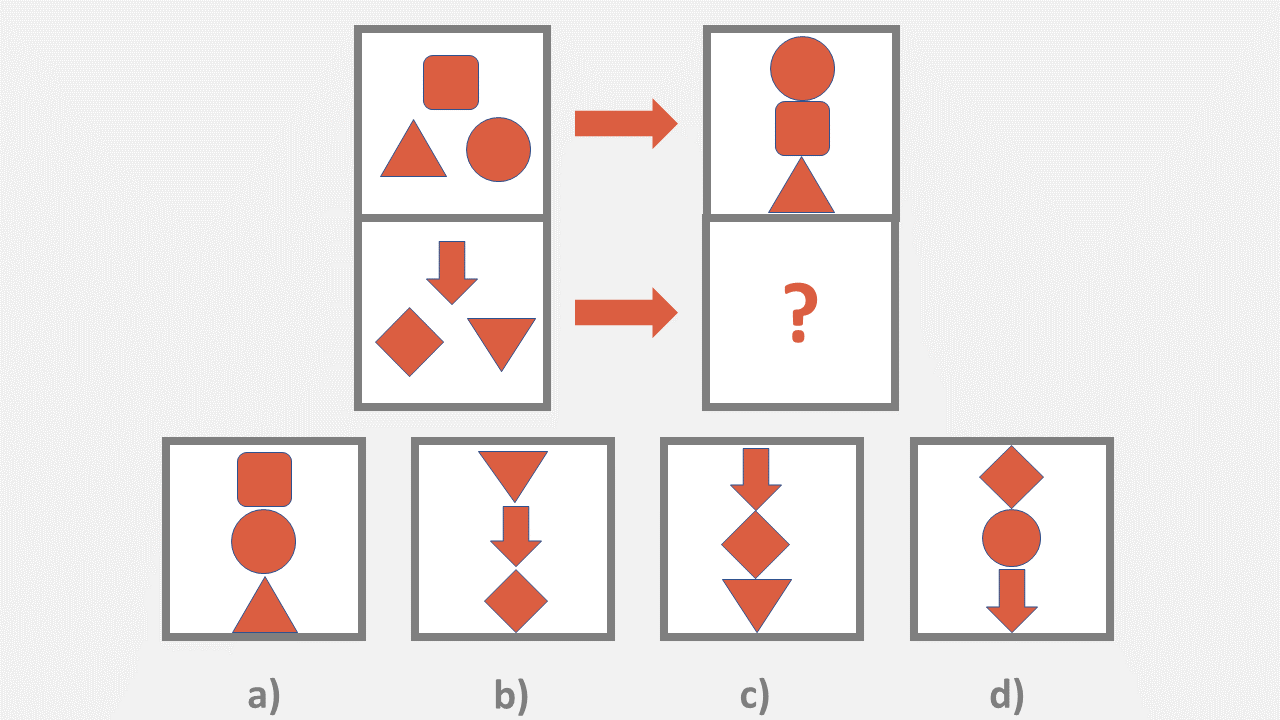

OLSAT Pattern Matrix
In a similar way to the word and letter matrix in the verbal section, the pattern matrix is made up of a box, measuring 3 x 3, with a missing item.
Spotting the pattern used helps the student choose the right answer from the multiple-choice options.
1. Consider the matrix below. Choose which figure goes in the space.
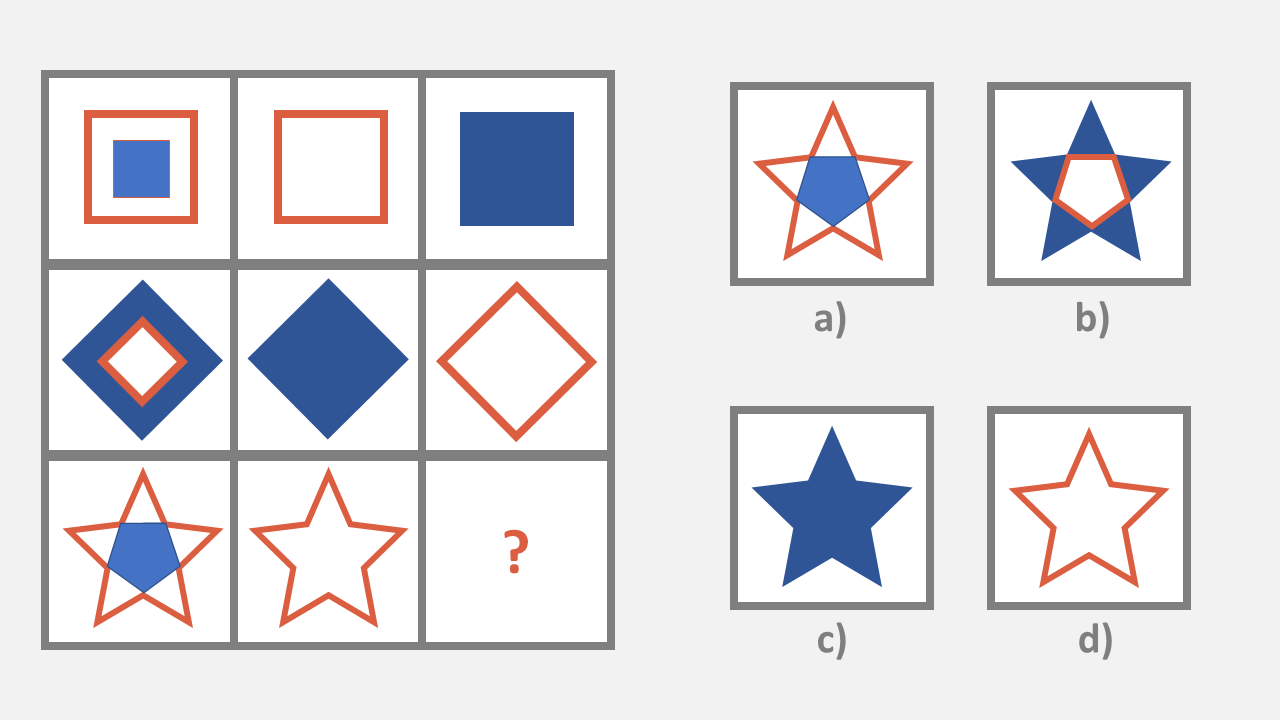
OLSAT Figural Series
The student will be presented with a series of four geometric shapes and will need to predict what the fifth shape will be, using the rule or pattern they have logically derived.
1. Select what the fifth shape in this series will be from the options.
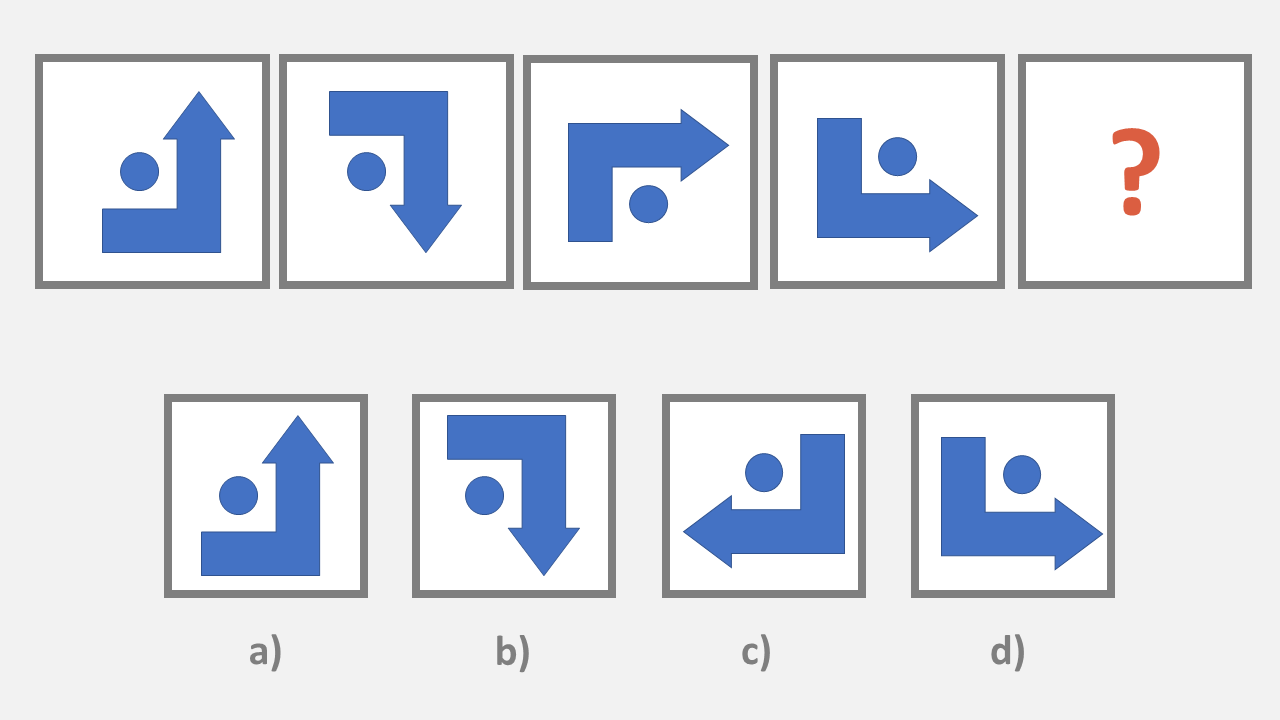
OLSAT Quantitative Reasoning
This section of questions focuses on the student’s understanding of the relationship between numbers, including using functions and making inferences.
OLSAT Number Series
In a number series question, the student will need to find the missing item in a sequence of numbers using the logical rule laid out by the other numbers. This is similar to the figural series question above.
1. Find the missing number in the following series:
2, 5, 9, 14, ?
a) 22
b) 20
c) 18
d) 15
OLSAT Numerical Inference
Working with numbers and number groupings, a student needs to demonstrate an understanding of relationships and how to find them to correctly choose the missing number in a group or sequence.
1. These two groups of numbers go together by following the same rule. Find the missing number.
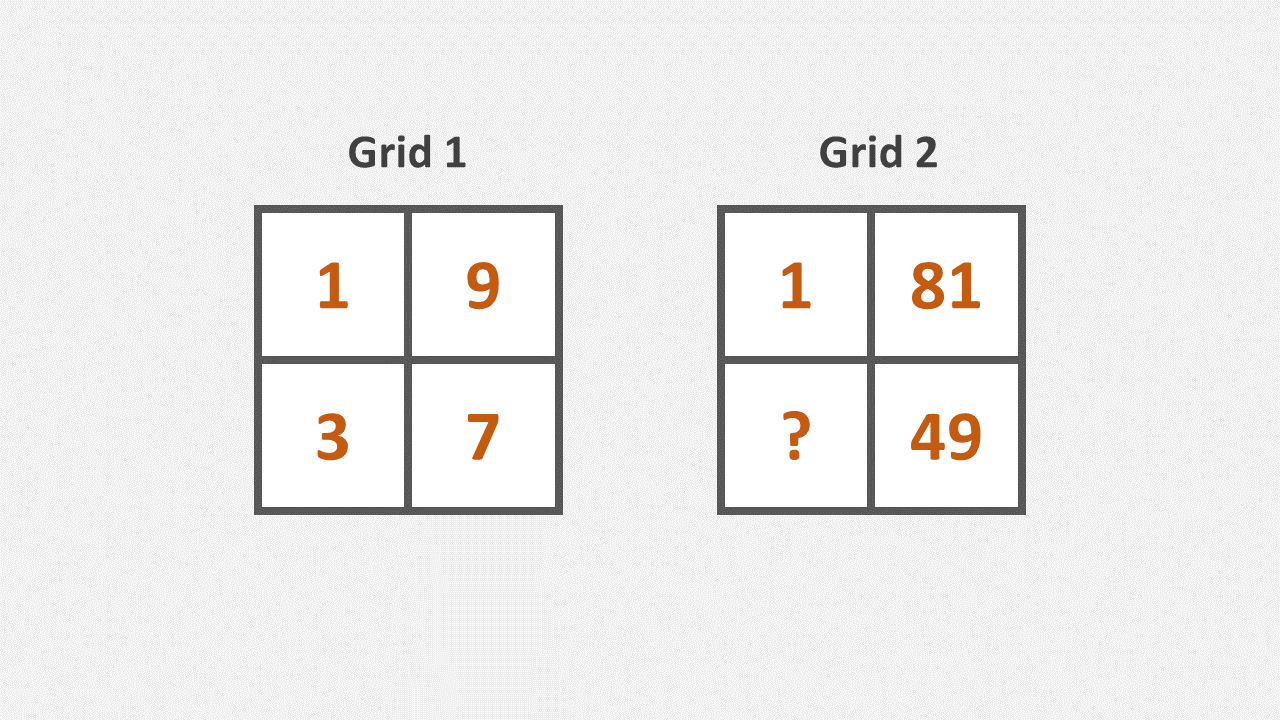
a) 7
b) 9
c) 12
d) 3
OLSAT Number Matrix
By discovering the pattern that governs the sequence in the 3 x 3 grid, a student will find that the number matrix questions are similar to other matrix questions – but these use digits instead of words or shapes.
1. Fill in the missing number from the grid.
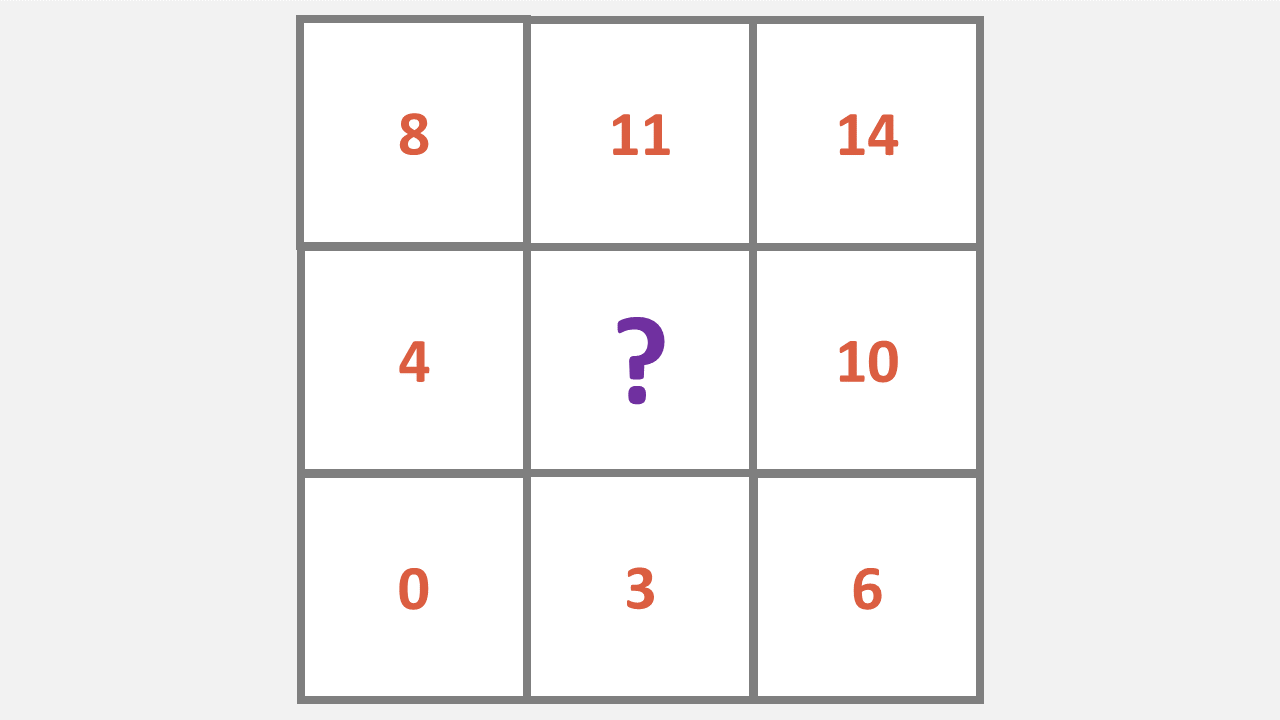
a) 5
b) 9
c) 18
d) 7
How to Prepare for the OLSAT Level E and F in 2025
Step 1. Take Practice Papers
Facing tests can be nerve-wracking, but one way to help your child feel more confident is through practice.
Seeing what the structure will be and what the questions will look like is bound to help them feel more secure.
Practice papers also help you to decide where any revision needs to be focused, by showing you and your child where they are struggling.
Step 2. Encourage Your Child to Create a Study Plan
Although helping your child to study seems like a great idea – and it is – it is also important that your child takes the initiative to study independently.
Making study a normal part of the day, through developing a study plan will help it feel less stressful and will avoid the feeling of ‘cramming’ just before the assessment.
Step 3. Go Through the First Few Questions With Your Child
Introducing different ways to answer questions is a great way to support your child in their revision.
You can go through the first couple of questions with them, talking about the importance of reading the question thoroughly so you understand it before starting.
Step 4. Go Through the Answers Together and Discuss
Practice tests will have answers available, so you can go through your child’s tests with them and discuss where they are doing well.
Working through practice questions can improve reasoning skills and this test preparation can make sure the student is ready for test day.
You can also talk through anything they find challenging, so you can look for new strategies and make a study plan to improve their chances at scoring highly.
Step 5. Teach Revision Tips
Every child learns differently, and your child will have developed problem-solving skills through education that you can reinforce at home.
As the OLSAT Levels E and F are multiple-choice tests, one of the techniques you could help your child with is elimination – deciding which answers are definitely incorrect.
Think about other techniques that are generally helpful when solving problems or puzzles, and see if you can find ways to encourage your child to use them in everyday life.
Step 6. Be Positive About the Test and Not Knowing the Answers
There are likely going to be questions that your child does not know the answer to – and there will probably be questions that you don’t know the answer to, as well.
This is fine, and it is important that you are positive about the whole experience rather than putting too much pressure on your child to do well.
All you can ask of them is to try their best.
Step 7. Make Sure Your Child Is Getting Enough Rest and Nutrition
Healthy children perform at their best – and you can help ensure that they are getting all the nutrition and sleep they need.
Regular meals, plenty of water to drink and a regular bedtime are all important to the overall health of your child, as well as their performance.
Prepare for OLSAT Test Level E and F with Test Prep Online
How Are the OLSAT Level E and OLSAT Level F Scored?
The OLSAT (Otis-Lennon School Ability Test) Level E and Level F are both cognitive ability tests designed to assess the abilities and aptitudes of students in different grade levels.
These tests are commonly used for admissions into gifted and talented programs or for identifying students' strengths and areas of improvement.
The OLSAT Level E is typically administered to students in grades 4 and 5, while the OLSAT Level F is administered to students in grades 6 and 7.
The scoring of the OLSAT tests is based on a percentile rank system. Each student's performance is compared to that of a nationally representative sample of students in the same grade level.
The percentile rank indicates the percentage of students in the sample who scored lower than the student.
For example, if a student receives a percentile rank of 75 on the OLSAT Level E, it means that they performed better than 75% of students in the sample for that grade level.
The OLSAT scores are also accompanied by a Standard Age Score (SAS). The SAS is a standardized score that compares the student's performance to the average performance of students at the same age level.
The average SAS is typically set at 100, and scores above or below 100 indicate performance above or below the average, respectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
No, the OLSAT is not an IQ test.
However, it does correlate to some important studies in intelligence factors, mostly regarding potential and aptitude.
It is a type of aptitude test that measures the way your child thinks more than what they know.
It is a nationally standardized and norm-referenced assessment that demonstrates how a child will perform in the future, rather than being based on what they have been taught in school.
There are two sections on the OLSAT Level E and the OLSAT Level F.
In the verbal section, questions cover verbal comprehension and verbal reasoning, while the non-verbal section covers figural reasoning and quantitative reasoning.
All the questions are multiple-choice.
A ‘good’ score on the OLSAT is difficult to quantify, as this can change depending on the gifted and talented program or specialized school that has been applied to.
Most programs look for the top 2-3% of students, so a score of 97th percentile or above is considered to be good enough.
This is an aptitude assessment, rather than something that is a snapshot of learning – and you can help them do as well as they can with practice.
Your child is allowed to prepare for the OLSAT Levels E and F.
You can help your child do well on the OLSAT Level E and Level F through encouragement and practice.
Online practice papers help to provide familiarity with the structure and type of questions, as well as signposting the right areas for revision.
You can be supportive and make sure that your child gets enough sleep and eats well, too.
There is no negative marking on the OLSAT, which means that your child will not get a negative mark if they get an answer wrong.
This means that your child can guess if they are not confident of an answer – it will give them more chance of getting it right than leaving it blank.
The specific score considered "gifted" can vary depending on the criteria set by different schools or organizations.
In general, a score at or above the 95th percentile is often considered indicative of giftedness. This means that a student scoring in the top 5% of test-takers would typically be considered gifted based on their OLSAT score.
However, it's important to note that the determination of giftedness is not solely based on a single test score and may involve additional assessments or evaluations by professionals in the field of gifted education.
Final Thoughts
The OLSAT Levels E and the OLSAT Level F are used as a standardized way of assessing a student on their general mental aptitude, logical thinking and problem solving – and this is why they are a reliable part of the application process for some specialist schools and gifted and talented programs.
The OLSAT can be prepared for – students should learn the type of questions that they are going to face in the assessment using practice papers.
This will not only ensure that they are familiar with the structure, but will also help them make the most of their revision time to perform at their absolute best.
Crucially, parents must remember that this can be an incredibly stressful time, even for high-achieving students, so encouragement, love and support are really important throughout their revision and test-taking.





